 Performs a sum s of the items chosen from two summable series A and B. If there are more than 2 summable series, they will be drawn randomly. The SUM instruction allows you to choose the subject heading.
Performs a sum s of the items chosen from two summable series A and B. If there are more than 2 summable series, they will be drawn randomly. The SUM instruction allows you to choose the subject heading.
To use it, you therefore need at least two summable series.
To facilitate resolution, Booleans are recommended.
Summable series: series whose items can be added together because they share the same units.
Example: quantity of nuts and quantity of apples , expressed in kg.
NB: on Actilud all summable series are assumed to share the same units.
Orchard Riddle
Bertha harvests 40kg of nuts and apples.
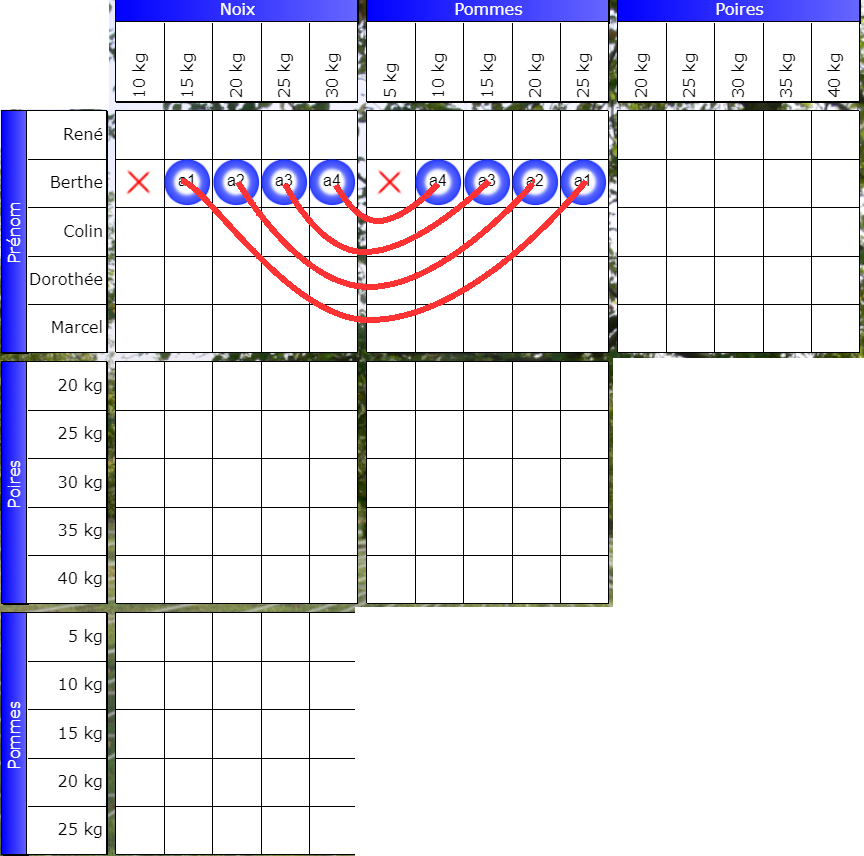
The red lines represent the relationships between the boxes across the grids, materialized by the Booleans.
False signs
Those present in the Boolean rows indicate that these positions are not available. If Bertha picks up 10kg of nuts, she cannot get 40kg by adding apples; similarly, if she picks up 5kg of apples, she cannot get 40kg by adding nuts.
Designer

Randomly selects two summable series. The subject is chosen from the other series – this is the random choice – or its heading can be imposed.
![]()
Isolated: If the instruction operates in isolated mode, the designer does not select rows that already contain signs, including Booleans.
![]()
Maximum number of executions of this instruction.
Formal proposal generated
a: B + C = s
Berthe: nuts + apples = 40
a: subject item
B,C: headings of the summable series
s: value of the sum in units of A and B.
